Calculate the median smoothing of a time series (SPMF documentation)
This example explains how to calculate the median smoothing of a time series using the SPMF open-source data mining library.
How to run this example?
- If you are using the graphical interface, (1) choose the "Calculate_median_smoothing_of_time_series" algorithm, (2) select the input file "contextMovingAverage.txt", (3) set the separator to the comma ',' (4) set the window size to 3, and then (5) click "Run algorithm".
- If you want to execute this example from the command line,
then execute this command:
java -jar spmf.jar runCalculate_median_smoothing_of_time_series contextMovingAverage.txt output.txt 3 ,
in a folder containing spmf.jar and the example input file contextMovingAverage.txt. - If you are using the source code version of SPMF, to run respectively this example, launch the file "MainTestMedianSmoothingFromFileToFile.java"in the package ca.pfv.SPMF.tests.
What is the calculation of the median smoothing of a time series?
Calculating the median smoothing (also called "1D median smoothing filter") of a time series is a simple but popular way of smoothing a time series to remove noise. It takes as parameter a window size w (a number of data point), which must be greater than 1. Then, if w is odd, the median smoothing of a time series is obtained by replacing each data point X by the median of the set of points consisting of X and the (w-1)/2 data points appearing before, and the (w-1)/2 data points appearing after. In the case where w is even, the median smoothing of a time series is obtained by replacing each data point X by sorting the values in the set of points consisting of X and the (w-2)/2 data points appearing before, and the 1+ (w-2)/2 data points appearing after, and taking the average of the two middle values in that set.
Note that if the original time series contains n points and w is odd, the median smoothing of the time series will contains (n - (w-1)) points. And if the original time series contains n points and w is even, the median smoothing of the time series will contains (n - (w-2) - 1) points.
What is the input of this algorithm?
The input is one or more time series. A time series is a sequence of floating-point decimal numbers (double values). A time-series can also have a name (a string).
Time series are used in many applications. An example of time series is the price of a stock on the stock market over time. Another example is a sequence of temperature readings collected using sensors.
For this example, consider the following time series:
| Name | Data points |
| ECG1 | 3,2,8,9,8,9,8,7,6,7,5,4,2,7,9,8,5 |
This example time series database is provided in the file contextMovingAverage.txt of the SPMF distribution.
In SPMF, to read a time-series file, it is necessary to indicate the "separator", which is the character used to separate data points in the input file. In this example, the "separator" is the comma ',' symbol.
To calculate the median smoothing, it is necessary to provide a window size w, which is a number of data points. In this example, this parameter will be set to 3 data points. Thus, the median smoothing will be calculated for each of the above time series using a window size of 3 data points.
What is the output?
The output is the median smoothing of the time series received as input. If w is odd, the median smoothing of a time series is obtained by replacing each data point X by the median of the set of points consisting of X and the (w-1)/2 data points appearing before, and the (w-1)/2 data points appearing after. In the case where w is even, the median smoothing of a time series is obtained by replacing each data point X by sorting the values in the set of points consisting of X and the (w-2)/2 data points appearing before, and the 1+ (w-2)/2 data points appearing after, and taking the average of the two middle values in that set.
For example, in the above example, if the window size is set to 3 data points, the result is:
| Name | Data points |
| SERIES1_CEMEDSMT | 3.0 8.0 8.0 9.0 8.0 8.0 7.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 4.0 7.0 8.0 8.0 |
To see the result visually, it is possible to use the SPMF time series viewer, described in another example of this documentation. Here is the original time series and the central moving average for window = 3.
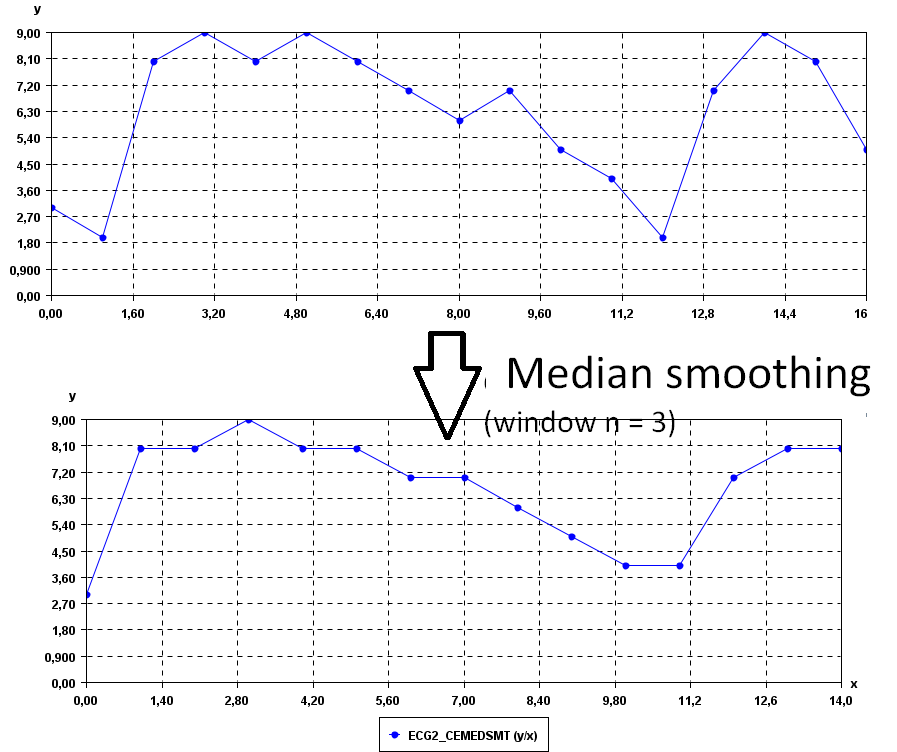
It is possible to see that the time series are less noisy.We can increase the values of the window parameter to obtain a yet more smooth time series. For example, if we set window = 7:
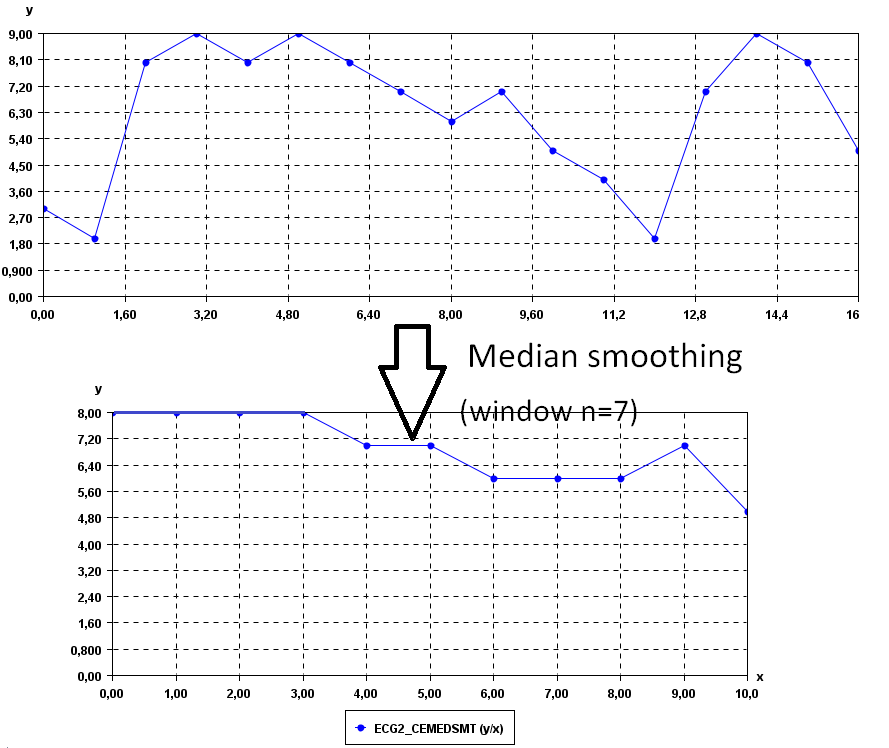
Input file format
The input file format is defined as follows. It is a text file. The text file contains one or more time series. Each time series is represented by two lines in the input file. The first line contains the string "@NAME=" followed by the name of the time series. The second line is a list of data points, where data points are floating-point decimal numbers separated by a separator character (here the ',' symbol).
For example, the input file of the previous example, named contextMovingAverage.txt is defined as follows:
@NAME=ECG2
3,2,8,9,8,9,8,7,6,7,5,4,2,7,9,8,5
Consider the first two lines. It indicates that the first time series name is "ECG2" and that it consits of the data points: 3,2,8,9,8,9,8,7,6,7,5,4,2,7,9,8, and 5. Then, three other time series are provided in the same file, which follows the same format.
But note that it is possible to have more than one time series per file. For example, this is another input file called contextSax.txt, which contains 4 time series.
@NAME=ECG1
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
@NAME=ECG2
1.5,2.5,10,9,8,7,6,5
@NAME=ECG3
-1,-2,-3,-4,-5
@NAME=ECG4
-2.0,-3.0,-4.0,-5.0,-6.0
Output file format
The output file format is the same as the input format. For example, there is the result for window = 3:
@NAME=ECG2_CEMEDSMT
3.0,8.0,8.0,9.0,8.0,8.0,7.0,7.0,6.0,5.0,4.0,4.0,7.0,8.0,8.0
Where can I get more information about the central moving average?
The median smoothing e is a basic operation for analyzing time series. It is described in many websites and books.